Computerized systems for monitoring and controlling movements GOODS UNDER SUSPENSION OF EXCISE
1. Introduction
2. The aim of EMCS
3. Legal framework
4. Benefits from the implementation of EMCS
5. The baseline product distribution with EMCS
6. Timetable for EMCS
7. Related Vocabulary
8. Contact
9. Connections
10. Forms, Files
11. Technical specifications for operators
1. Introduction
The EMCS is a computerized system for the monitoring and controlling of intra-Community movements of harmonized products (energy, tobacco and alcoholic products) under suspension of payment of excise duties. The main function of this system is the electronic submission of the Administrative Document (e-AD), which replaces the paper based, Accompanying Administrative Document (AAD), which previously accompanied such movements.
The system was developed by all Member States based on specifications agreed between the Member States and the EU Commission.
- Functional Requirements - Functional Excise System Specifications (FESS).
- Requirements Planning and Development-Design Document for National Excise Application (DDNEA).
2. The aim of the EMCS
The ultimate goal of the system is to improve the functioning of the internal market. With this system it is possible for Member States to monitor in real time the movements of harmonized goods under suspension of excise duties, and carry out the necessary checks to ensure the collection of the duties, in the Member State where the products are consumed, and therefore reducing the risk of fraud.
3. Legal framework
- The Decision No 1152/2003/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 June 2003 on computerizing the monitoring of the movements of products subject to excise goods under suspension of excise duties.
- The Council Directive 2008/118/EC of 16 December 2008, which came into force on 1 April 2010, concerning the general arrangements for excise duties, regulating the electronic monitoring and controlling of the movements of harmonized goods under suspension of excise duties. This Directive repealed Directive 92/12/EEC.
- The Commission Regulation (EC) 684/2009 of 24 July 2009 implementing Council Directive 2008/118/EC as regards the computerized procedures for the movement of products, under suspension of excise duties.
- The Council Regulation (EU) No. 389/2012 of 2 May 2012 on administrative cooperation in the field of excise duties, repealing Regulation (EC) No 2073/2004.
- The Excise Duties Law 91 (I) / 2004, associated National instructions, Orders and Notifications.
4. Benefits from the implementation of EMCS
- Simplify procedures by using electronic submission of the e-AD. Abolishing the process of using an accompanying administrative document, and thus creating a timely and paperless environment between the economic operators, and the authorities.
- Immediate validation of electronic administrative document, ensuring that both the sender and the recipient are authorized to trade harmonized products under duty-suspension arrangements.
- Timely clearance of the movements and release of the relevant guarantees.
- Reducing the risk of fraud (false movements, involvement of economic operators unknowingly into "suspect" movements, etc.)
5. The basic scenario for the movement of products via EMCS
The movement of products subject to excise duties under suspensive arrangements within the Community, is initiated from an authorized warehouse keeper of a tax warehouse at the member state of dispatch:
(a) to an authorized warehouse keeper of the tax warehouse at the member state of destination,
(b) to a registered consignee at the member state of destination,
(c) to a temporary registered consignee at the destination member state,
(d) to exempted Organizations (Embassies, International Organizations, Armed Forces, etc.),
(e) in a place of direct delivery at the destination member state which will be designated by the authorized warehouse keeper or the registered consignee of the destination member state.
(f) for export
The Director can authorize a registered consignor, natural or legal entity, to act within the framework of their business, to send harmonized products under suspension, to the destinations listed above, released for free circulation after importation at the member state of dispatch.
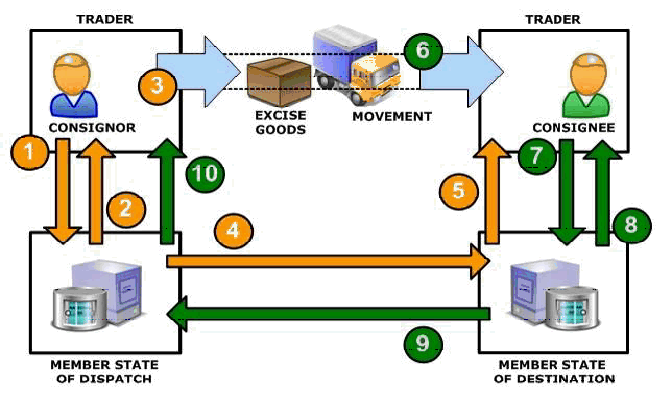
1. The sender of the e-AD submitted to the Authorities of the MS (dispatch).
2. The MS of dispatch validates and returns the e-AD back to the Consignor, bearing the unique reference code A.R.C. (AAD Reference Code); MC a unique code number validation ARC (AAD Reference Code). The e-thesis communicated to the sender.
3. The sender after receiving an MC certified with ARC, consigning goods.
4. KM sending forward the e-AD MS in receipt.
5. The MS notifies the receiving e-AD the recipient.
6. The harmonized products reach their destination.
7. The recipient shall report the receipt to the Principles of KM receipt.
8. The MS confirms receipt of the report of receipt and send a certified back to the recipient.
9. KM receipt forward the validated reference received the MS mission.
10. The MS notifies the sender sending the report of receipt and release the security mission.
6. Timetable for EMCS
The EMCS system has been placed in production on the 1st of April 2010.
Minimum equipment requirements:
The minimum equipment requirements needed by operators to be able to use the EMCS online are the following:
- Active Cookies
- Activation of Javascript
- Minimum screen resolution 1024x768
- Internet browser (Mozilla Firefox 2.xx/3.xx, Internet Explorer 8/9, Opera 9.xx, etc.)
- Acrobat PDF Reader (for printing reports)
7. Related Vocabulary
| Vocabulary definitions |
| ARC-AAD Reference Code |
| AAD-Administrative Accompanying Document |
| AWK-Authorized Warehouse Keeper |
| C.nee-Consignee (Recipient) |
| C.nor-Consignor (Sender) |
| DDNEA-Design Document National Excise Application |
| Destination-Member State of destination for the movement |
| Dispatch-Send harmonized products under suspension (without payment of excise duties) |
| EMCS- Excise Movement and Control System. Machine monitoring system. & Control movements of goods under suspension of payment of excise duty. |
| e-AAD, e-AD-Electronic Administrative Document |
| EU-European Union |
| Exc.D.-Excise Duties(Special) Consumption tax |
| Excise Goods-Products subject to specific excise duties |
| FESS-Functional Excise System Specifications |
| MS-Member State |
| Rcee-Registered Consignee (ex Registered Trader) |
| RCor-Registered Consignor |
| RoR-Report of Receipt |
| SEEDSystem of Exchange of Excise Data |
| TRC-Temporary Registered Consignee |
| TW-Tax Warehouse |
| Ec.Op.-Economic Operator |
8. Communication
For more information, you may write to the following address.
E-mail: headquarters@customs.mof.gov.cy
9. Connections
You can connect to the Training an External Testing Environment or with the Production Environment of E.M.C.S. system clicking on the appropriate title.
The website of the Directorate General for Taxation and Customs Union of the European Commission provides additional information on the EMCS system. It also includes links to the websites of Member States on the subject of EMCS.
10. Forms, Files
An economic operator may apply for access rights to the computerized system EMCS using form C. 1003B (only in greek). The form duly completed must be submitted at the local Customs Office or directly to the Excise Duties Section at Customs headquarters.
11. Specifications for traders
Please click on the related file:
1. User Manual for EMCS,
2. EMCS phase 3 messages for economic operators,
3. EMCS phase 3 messages for economic operators (Appendix B),
4. EMCS XSDs for phase 3.